 Since the prehistoric times the use of a diverse range of materials has been one of the characteristic features of humankind. Human civilisation found its identity in many materials as evident from the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and then the Iron Age; each era is defined by new material. In the present world, it would not be wrong to say that modern civilisation is characterised by Cement.4Notably, concrete is the most consumed resource on earth after water. The earliest evidence of cementing materials dates to the construction marvels created by Egyptians and to the architecture of the Roman Empire. The Industrial Revolution marked an exponential rise in the use of cement and iron/steel for modern architecture, which continues to grow to date.
Cement is a fine powdered substance used as an intermediate binding agent in construction activities. It is a manmade material comprising of limestone, clays, shells, silica sand, etc processed together in a controlled environment (around 1500 °C). Cement is a manmade wonder, which sets, hardens and brings strength to the constructed structures over time through its peculiar adhesive and tensile properties. This makes it an indispensable component of building materials, such as – Mortar and Concrete. The former is a mixture of cement and other fine aggregates. It is mainly used for masonry activities. The latter is a composite material made up of cement mixed with aggregates (sand, gravel, other additives) and water; it is the most extensively used construction and building material for a wide range of structures.5
Since the prehistoric times the use of a diverse range of materials has been one of the characteristic features of humankind. Human civilisation found its identity in many materials as evident from the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and then the Iron Age; each era is defined by new material. In the present world, it would not be wrong to say that modern civilisation is characterised by Cement.4Notably, concrete is the most consumed resource on earth after water. The earliest evidence of cementing materials dates to the construction marvels created by Egyptians and to the architecture of the Roman Empire. The Industrial Revolution marked an exponential rise in the use of cement and iron/steel for modern architecture, which continues to grow to date.
Cement is a fine powdered substance used as an intermediate binding agent in construction activities. It is a manmade material comprising of limestone, clays, shells, silica sand, etc processed together in a controlled environment (around 1500 °C). Cement is a manmade wonder, which sets, hardens and brings strength to the constructed structures over time through its peculiar adhesive and tensile properties. This makes it an indispensable component of building materials, such as – Mortar and Concrete. The former is a mixture of cement and other fine aggregates. It is mainly used for masonry activities. The latter is a composite material made up of cement mixed with aggregates (sand, gravel, other additives) and water; it is the most extensively used construction and building material for a wide range of structures.5
A typical composition of Ordinary Portland Cement combines calcareous materials (or calcium carbonate) and argillaceous substances (silicates of alumina) crushed and ground together above 1500º C to form a uniform powder (in the dry process) or a homogenous paste (through the wet process).6 Figure illustrates the principle ingredients of cement whose characteristic properties are described as follows:
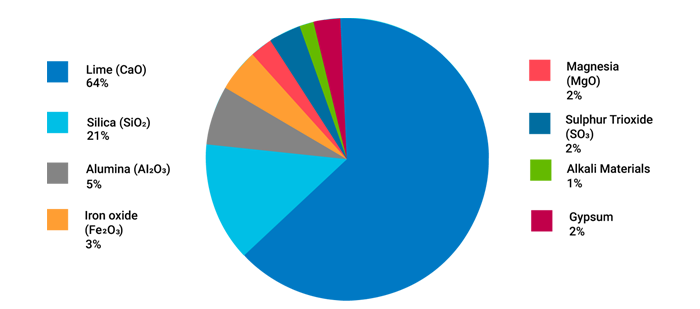








 Each constituent of the cement material undergoes chemical reactions at high temperatures inside cement kilns during the manufacturing process. The resultant compounds are popularly known as Bogue compounds. There are mainly four types of compounds:
Each constituent of the cement material undergoes chemical reactions at high temperatures inside cement kilns during the manufacturing process. The resultant compounds are popularly known as Bogue compounds. There are mainly four types of compounds:
Their proportion controls the chemical properties of cement in terms of strength and settling properties. Most cements are hydraulic in nature, ie, they set in the presence of water and release heat due to reactions between these components. A certain category of cement is non-hydraulic where they set in dry form and reaction occurs in the presence of carbondioxide in the air. The latter category is meant for specialised applications such as resistance to chemicals, etc. This section highlights the chemical process associated with commonly used Portland cement, which is a form of a hydraulic type of cement. The following steps illustrate chemical reactions, which govern the settling and hardening properties of the cement when applied to a construction structure.9
Read more

These materials can be added to the concrete as they contribute to the hardening process due to their hydraulic and pozzolanic properties. The most commonly used SCMs are:
The Cement industry is the only industry that demonstrates a great example of converting ‘waste to wealth’ by making use of rejects from other industries. Over time, the Cement Industry has created several opportunities around the optimisation of resources and energy inputs. The Indian Cement sector is at the forefront of energy and fuel efficiency related innovation with a performance at par with the best available technologies globally. Moving forward, supporting policy frameworks will enable more advances in the sector.
Less more