A Star Rating system has been introduced by the Ministry of Mines, Government of India, to assess and verify best performing mines in the country following stringent assessment parameters of Sustainable Development Framework (SDF). The Ministry of Mines aims to encourage mining operations that are financially viable; socially responsible through community engagement and welfare programmes; environmentally, technically and scientifically sound; with a long-term view of development; uses mineral resources responsibly; and, ensures sustainable post closure land uses.
Mining is a highly complex and technical process. It begins with exploration; continues through production; followed by closure and supporting post mining land use. Each stage requires scientific planning and proficient execution of activities from overall sustainability standpoint. Mining serves the community by way of supporting local health, education, generating direct employment and providing raw material to the downstream industrial value chains.
India is among the world’s leading producers of limestone, directly catering to the needs of domestic Cement Industry. Over 95% of limestone mineral is extracted through captive mines, mostly operated by the private sector cement companies. 1 It is significant to highlight that the Indian Cement Industry yet again demonstrated its technical prowess and socio-economic responsibility as it leads the charts of best performing mines under the Star Rating System. In the first round of online star rating assessment system, out of 560 applicants with working mines, 32 mines got a 5 Star rating largely represented by the Cement Sector.
By excelling at the Star Rating system assessment process, the Indian Cement Industry has objectified a built-in compliance mechanism in its mining operations setting benchmarks for the other industries. Cement Industry proficiently addresses all three core pillars of sustainable development illustrated in Figure below.
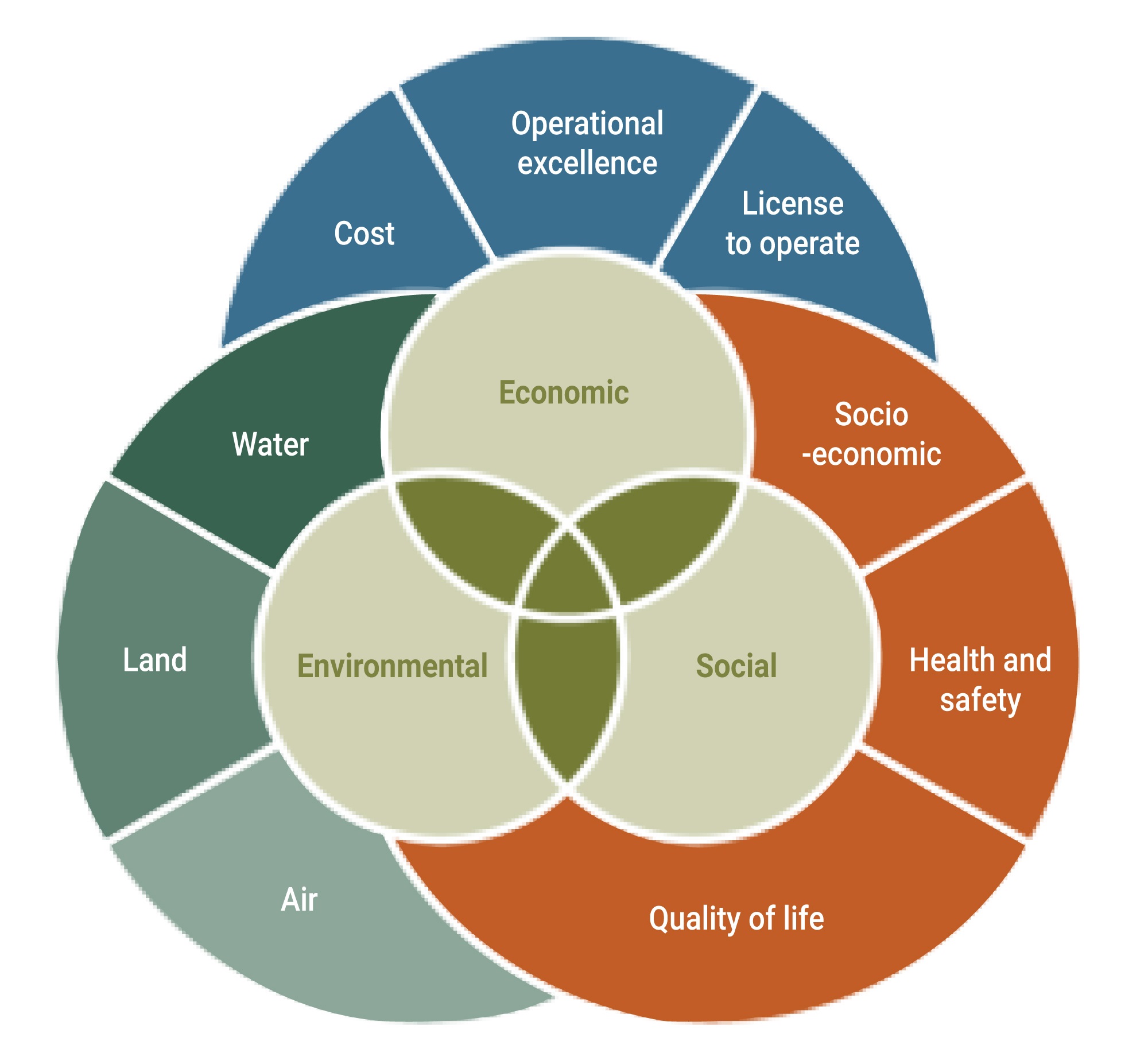
As a direct outcome of its adherence to the exhaustive parameters of Star Rating assessment system, the Indian Cement Industry has also showcased following direct benefits arising from its mining operations:
